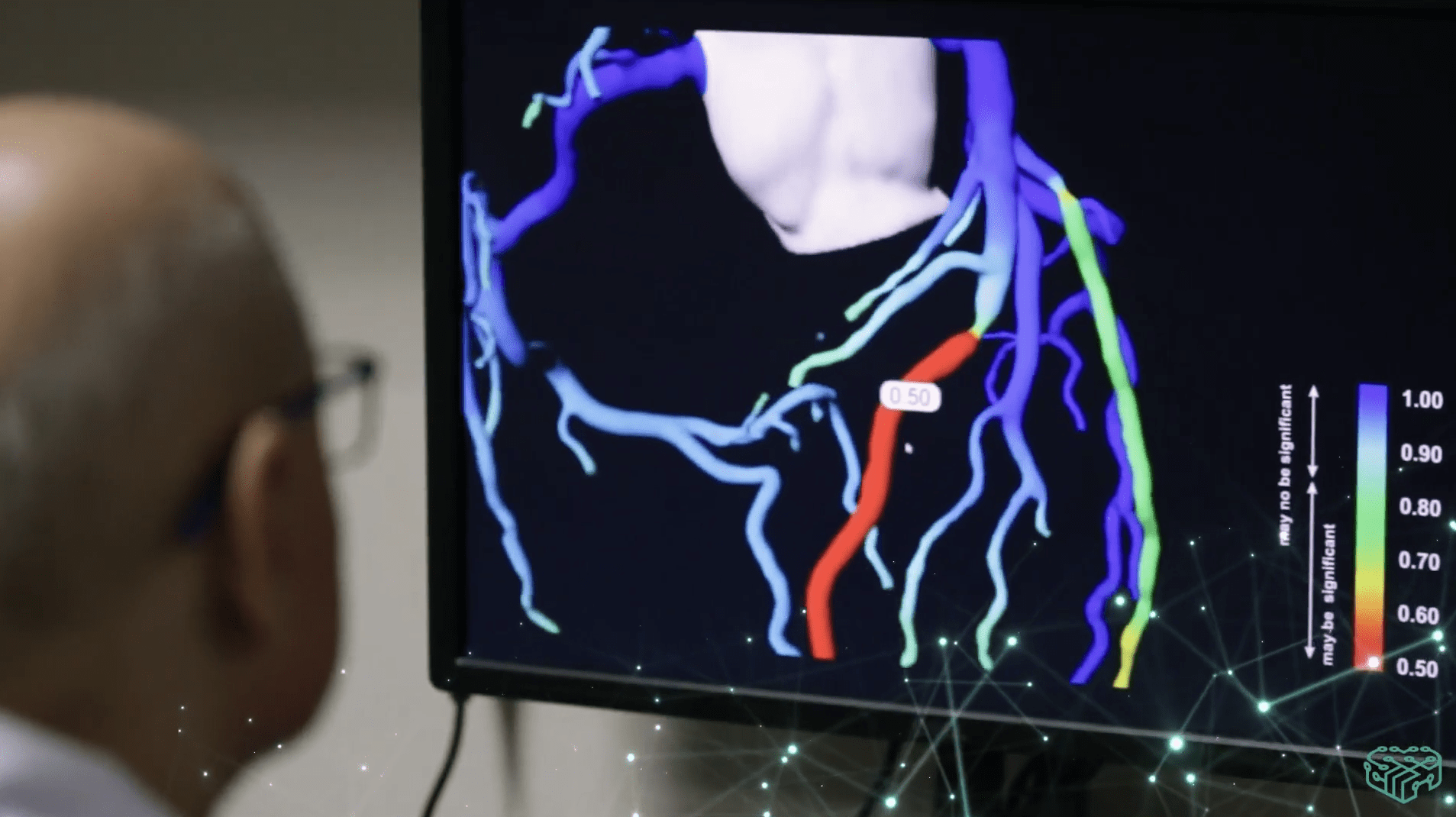
Our latest publication in Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology showcases the feasibility and functionality of our VCAST technology, a patented, AI-based medical system developed for non-invasive, clinical quantitative and qualitative analysis of CT-scan data, to assess the hemodynamic significance of coronary artery atherosclerotic stenosis.
Using a comparative method to simulate flow energy losses in real and reconstructed models of the coronary arteries, the study confirms the potential of medical image-based Computational Fluid Dynamic methods in the clinical setting for flow studies of the cardiovascular system. The publication presents results obtained from flow simulations in the coronary arteries of 25 patients with different degrees of stenoses and areas of occurrence. Both FFRsten and EFR indices showed a very significant positive correlation with coronary CT angiography-derived FFR, making this non-invasive, comparative test a promising tool for supporting the prevention and functional evaluation of coronary disease.
VCAST has several advantages over the invasive procedure used to obtain FFR, including being non-invasive, safer because has a lower radiation dose, and is a time & cost-effective solution for the functional evaluation of stenosed vessels. The VCAST technology offers a comprehensive evaluation of blood flow through the coronary arteries under stress test conditions, providing more diagnostic value than traditional methods. This breakthrough technology has huge market potential, as it could be used as an alternative to the invasive catheterization procedure currently used to obtain FFR.
Coronary artery disease is the most common type of heart disease in the US. About 20.1 million adults aged 20 and older have CAD. Therefore, Kardiolytics’ VCAST technology has the potential to revolutionize the prevention and treatment of this disease.